Private Health Insurance: Compare Plans, Costs & Benefits
Introduction to Private Health Insurance
Private health insurance serves as a vital component of the healthcare system in many countries, offering individuals and families the opportunity to access a range of medical services beyond those covered by public health systems. It allows for greater flexibility in choosing healthcare providers, faster access to treatments, and a wider array of services. In this article, we will dive into the different plans available, discuss the costs associated with private health insurance, and explore the benefits that come with having such coverage.
Understanding Private Health Insurance Plans
Private health insurance plans can vary significantly based on the provider, the coverage offered, and the specific needs of the insured. Generally, these plans can be categorized into several types, each catering to different healthcare needs.
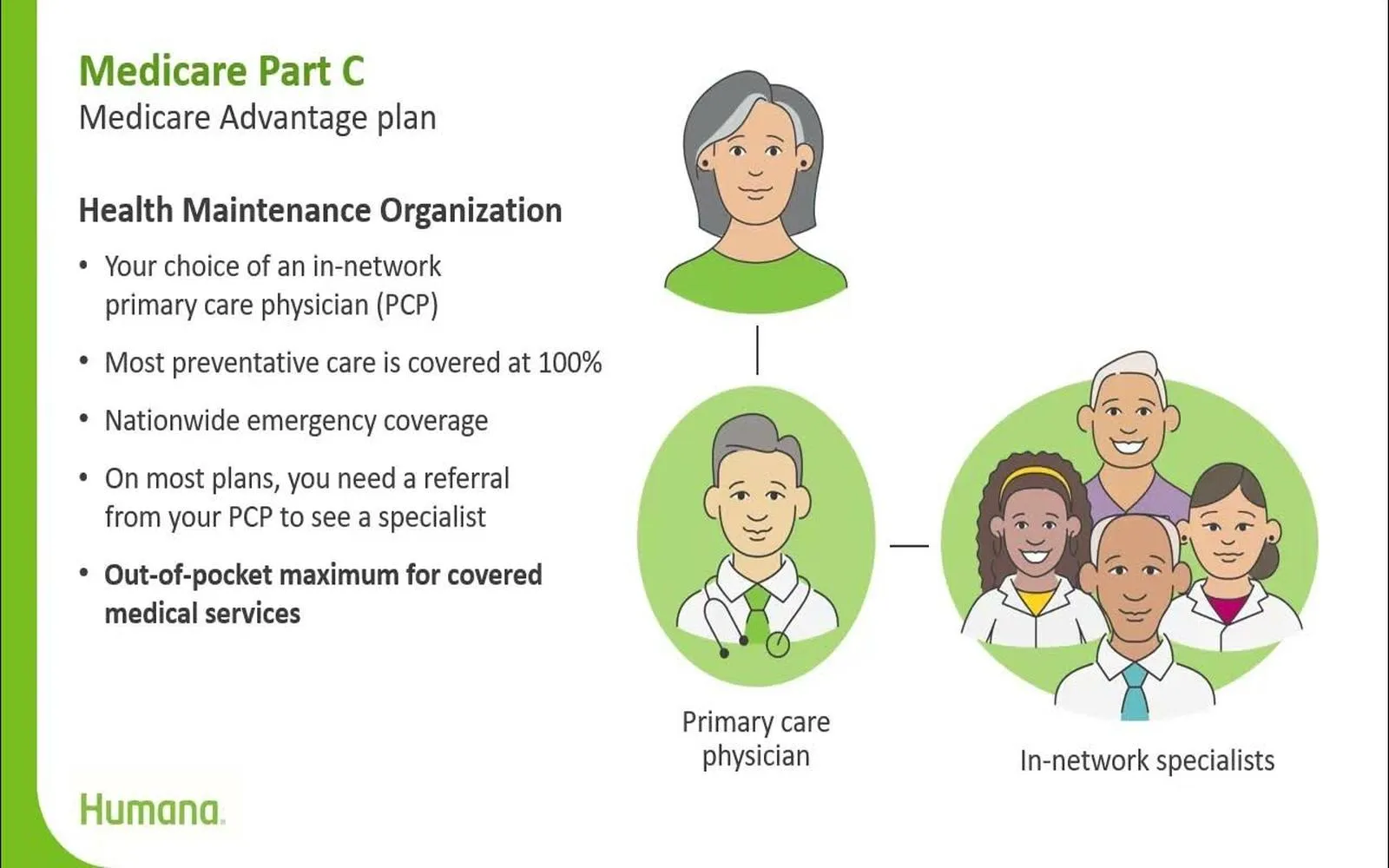
1. Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs)
HMOs are known for their cost-effective approach to healthcare. Members are required to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who acts as a gatekeeper for specialist services. While they often have lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs, HMOs generally require referrals for specialist visits and may limit coverage to network providers.
2. Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs)
PPOs offer more flexibility than HMOs. They do not require members to select a primary care physician or obtain referrals for specialists. PPO members can see any healthcare provider, although staying within the network typically results in lower costs. This option is ideal for those who value choice and convenience in their healthcare.
3. Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs)
EPOs combine elements of HMOs and PPOs. Members do not need a referral to see a specialist, but they must use the network of providers for coverage. While EPOs generally have lower premiums than PPOs, they offer less flexibility since out-of-network services are not covered.
4. Point of Service (POS) Plans
POS plans are a hybrid of HMO and PPO models. Members select a primary care physician and need referrals to see specialists, similar to HMOs, but they have the option to receive care outside of the network at a higher cost, akin to PPOs. This plan type is suitable for individuals who want a balance between cost and flexibility.
5. High Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs)
HDHPs are designed for individuals who want lower premiums and are willing to pay higher out-of-pocket costs before insurance kicks in. They are often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), allowing members to save money tax-free for medical expenses. HDHPs are ideal for those who are generally healthy and do not expect frequent medical care.
Comparing Costs of Private Health Insurance
The cost of private health insurance can vary widely based on factors such as the type of plan, the level of coverage, the age of the insured, and geographic location. When considering private health insurance, it’s essential to understand the various components that contribute to overall costs.
1. Premiums
The premium is the monthly cost of maintaining your health insurance coverage. This amount can be influenced by the type of plan you choose, your age, and the number of dependents covered. Generally, HMOs have lower premiums compared to PPOs, but this often comes with trade-offs in terms of flexibility and provider choice.
2. Deductibles
The deductible is the amount you must pay out-of-pocket before your insurance starts covering costs. Plans with high deductibles typically have lower premiums, while those with lower deductibles usually have higher premiums. Choosing the right deductible depends on your expected healthcare needs and financial situation.
3. Co-payments and Co-insurance
Co-payments (co-pays) are fixed fees you pay for specific services, like doctor visits or prescriptions, while co-insurance is a percentage of the costs you share with your insurer after meeting your deductible. Understanding these costs is crucial for budgeting your healthcare expenses.
4. Out-of-Pocket Maximums
The out-of-pocket maximum is the most you will pay for covered services in a policy year. Once you reach this limit, your insurance covers 100% of the costs for covered services. Knowing this limit helps you plan for unexpected healthcare expenses.
5. Network Considerations
The costs associated with using out-of-network providers can be significantly higher than using in-network providers. It’s essential to review a plan's network to understand how it affects overall costs and access to care.
Evaluating Benefits of Private Health Insurance
While costs are a significant factor in choosing private health insurance, the benefits provided by a plan can vastly impact your healthcare experience. Here are some key benefits to consider:
1. Access to a Broader Range of Services
Private health insurance typically covers a wider array of services compared to public health systems. This includes specialty care, elective procedures, and alternative treatments, which may not be fully covered by public insurance plans.
2. Shorter Wait Times
One of the most appealing aspects of private health insurance is the reduced wait times for treatments and procedures. Patients with private insurance often experience quicker access to specialists and elective surgeries, which can significantly impact patient satisfaction and health outcomes.
3. Flexibility in Provider Choice
Private health insurance offers the flexibility to choose your healthcare providers, including specialists. This choice empowers patients to seek care from professionals they trust, which can lead to better healthcare experiences and outcomes.
4. Personalized Care
With private health insurance, patients often receive more personalized care. Healthcare providers may have more time to spend with patients, leading to better communication and tailored treatment plans that align with individual needs.
5. International Coverage
Many private health insurance plans offer international coverage, which is particularly beneficial for travelers or expatriates. This feature ensures that you have access to medical care even when you are outside your home country.
Choosing the Right Private Health Insurance Plan
Choosing the right private health insurance plan requires careful consideration of your individual needs, lifestyle, and budget. Here are some steps to guide you through the selection process:
1. Assess Your Healthcare Needs
Begin by evaluating your current health status, any ongoing medical conditions, and your anticipated healthcare needs for the upcoming year. Consider factors such as frequency of doctor visits, prescription medications, and potential surgeries or specialist consultations.
2. Compare Plans
Once you have a clear understanding of your needs, compare different health insurance plans. Look at the premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximums. Pay attention to the plan networks and whether your preferred providers are included.
3. Consider Additional Benefits
Evaluate the additional benefits offered by each plan, such as wellness programs, preventative care coverage, and mental health services. These benefits can enhance your overall healthcare experience and may influence your decision.
4. Read Reviews and Ratings
Research customer reviews and ratings for the insurance providers you are considering. This feedback can provide insights into the quality of customer service, claims processing, and overall satisfaction with the plans.
5. Seek Professional Guidance
If you feel overwhelmed by the options, consider consulting with a licensed insurance broker. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your unique situation and help you navigate the complexities of private health insurance.
Conclusion
Private health insurance plays a crucial role in facilitating access to quality healthcare. By understanding the various plans available, comparing costs, and evaluating benefits, individuals can make informed decisions that best suit their healthcare needs. With careful consideration and research, you can find a private health insurance plan that provides the coverage and flexibility you desire, ensuring peace of mind for you and your family.
Explore
Humana Medicare Plans: Compare Coverage & Benefits

Get Instant Travel Insurance Quotes: Compare Plans & Save Today!

Best Personal Loan Offers: Compare Rates & Benefits

Comprehensive Guide to Humana Health Coverage Plans: Benefits, Options, and Enrollment Tips

Unlock Your Adventure: How to Easily Compare Travel Insurance Quotes Online

Compare AARP Insurance Quotes for Affordable Coverage
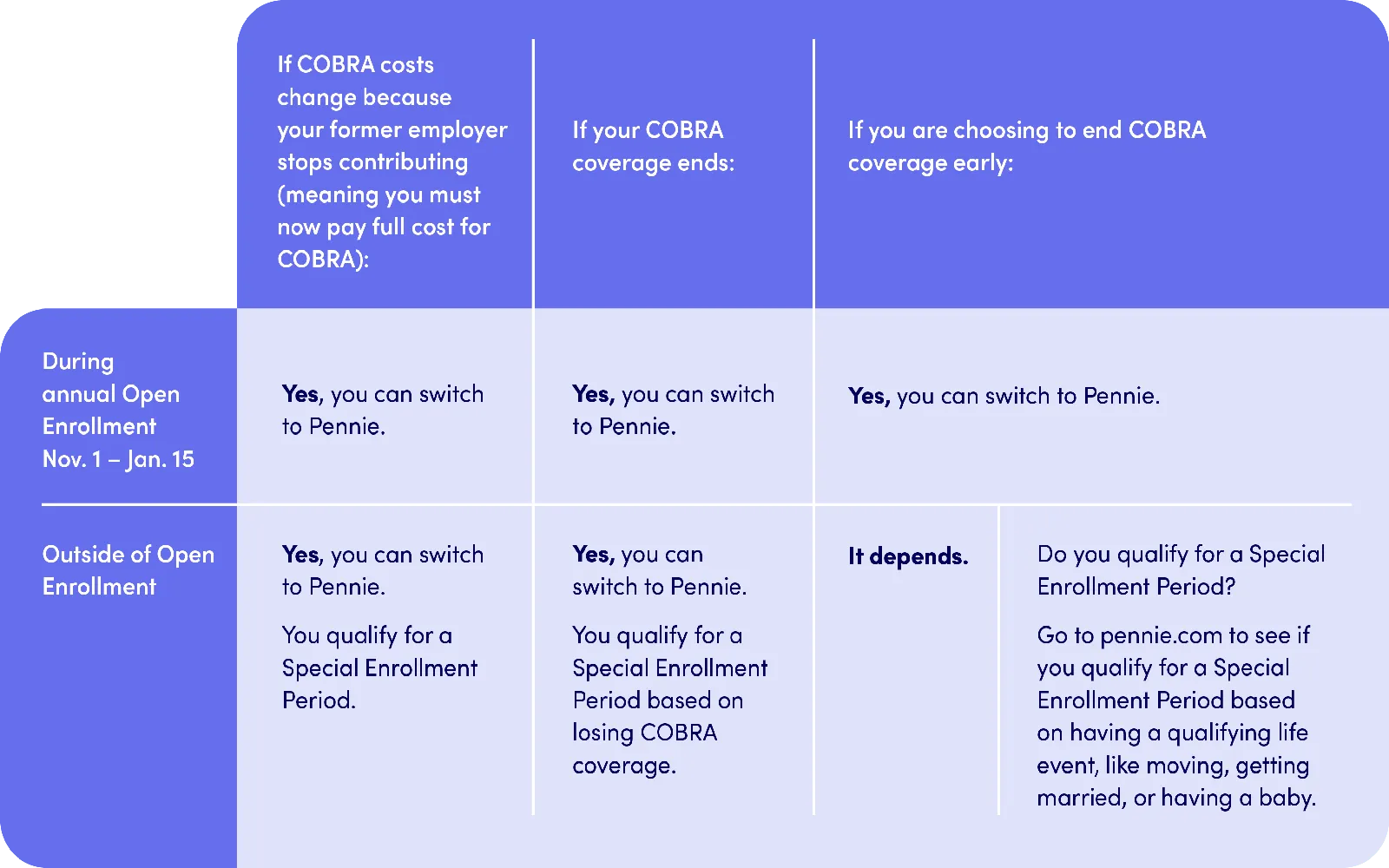
Pennie Insurance Explained: Your Guide to Pennsylvania’s Health Plans

Best Health Insurance Plans for Comprehensive Coverage
