Window Replacement Options: A Comprehensive Guide
Replacing windows can dramatically enhance the aesthetic appeal, energy efficiency, and overall comfort of your home. With numerous options available, choosing the right type of window for your needs involves considering factors like material, style, energy efficiency, and budget. This guide provides an overview of popular window replacement options to help you make an informed decision.
1. Types of Window Materials
The material of your windows affects their durability, maintenance, and energy efficiency. Here are the most common materials used in window construction:
1.1 Vinyl Windows
Overview: Made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC), vinyl windows are known for their durability and low maintenance requirements.
Advantages:
- Energy Efficiency: Often equipped with insulating glass and multi-chambered frames to improve energy efficiency.
- Low Maintenance: Resistant to peeling, chipping, and cracking. Requires only occasional cleaning.
- Cost-Effective: Generally more affordable than wood or fiberglass options.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Aesthetic Options: Less variety in styles and colors compared to wood.
- Can’t Be Painted: Limited ability to customize the appearance with paint.
1.2 Wood Windows
Overview: Traditional and aesthetically pleasing, wood windows offer a classic look and natural insulation.
Advantages:
- Aesthetic Appeal: Warm and natural appearance with the ability to be stained or painted.
- Customizable: Offers a wide range of styles and finishes.
Disadvantages:
- Maintenance: Requires regular painting or staining to protect against the elements and prevent rot.
- Cost: Generally more expensive than vinyl or aluminum windows.
1.3 Fiberglass Windows
Overview: Made from fiberglass composite materials, these windows are known for their strength and energy efficiency.
Advantages:
- Durability: Resistant to warping, cracking, and fading. Suitable for extreme weather conditions.
- Energy Efficiency: Offers excellent insulation properties and can improve energy savings.
- Low Maintenance: Minimal upkeep compared to wood windows.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: Typically higher in price compared to vinyl and aluminum windows.
- Limited Customization: Fewer options for color and style compared to wood.
1.4 Aluminum Windows
Overview: Constructed from aluminum, these windows are known for their strength and slim frames.
Advantages:
- Durability: Strong and resistant to the elements, making them ideal for high-traffic areas.
- Modern Appearance: Sleek and slim frames suitable for contemporary designs.
Disadvantages:
- Insulation: Poor thermal insulation compared to other materials. Often requires a thermal break to improve energy efficiency.
- Maintenance: Can be prone to corrosion if not properly treated.
2. Types of Window Styles
Window styles impact the functionality, aesthetics, and ventilation of your home. Here are popular window styles to consider:
2.1 Double-Hung Windows
Overview: Feature two sashes that slide vertically, allowing both the top and bottom sections to open.
Advantages:
- Ventilation: Provides good ventilation as both sashes can be opened.
- Ease of Cleaning: Many models tilt inward for easy cleaning of both sides.
Disadvantages:
- Energy Efficiency: Older models may have less effective insulation compared to newer designs.
2.2 Casement Windows
Overview: Hinged on one side and open outward like a door.
Advantages:
- Energy Efficiency: Provides a tight seal when closed, enhancing energy efficiency.
- Ventilation: Offers excellent ventilation and unobstructed views.
Disadvantages:
- Space: Requires space outside to open fully, which may not be ideal for all locations.
2.3 Sliding Windows
Overview: Feature one or more sashes that slide horizontally.
Advantages:
- Ease of Use: Simple operation and suitable for large openings.
- Unobstructed View: Minimal framing allows for clear views.
Disadvantages:
- Ventilation: Limited to half of the window opening for ventilation at a time.
2.4 Bay and Bow Windows
Overview: Extend outward from the wall, creating a bay or bow effect.
Advantages:
- Aesthetic Appeal: Adds architectural interest and expands interior space.
- Natural Light: Maximizes the amount of natural light entering the room.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: Generally more expensive due to the complexity of installation.
- Maintenance: May require additional upkeep compared to standard window styles.
2.5 Awning Windows
Overview: Hinged at the top and open outward, often used in combination with other window types.
Advantages:
- Ventilation: Provides good ventilation even during rainy weather.
- Privacy: Allows for ventilation while maintaining privacy.
Disadvantages:
- Space: Requires clearance outside for the window to open.
3. Energy Efficiency Considerations
When replacing windows, energy efficiency is a key factor to consider. Here are some features that enhance energy efficiency:
3.1 Low-E Glass
Overview: Coated with a thin layer of metal oxide to reduce heat transfer and UV radiation.
Advantages:
- Insulation: Helps keep homes warmer in winter and cooler in summer.
- UV Protection: Reduces fading of interior furnishings.
3.2 Double or Triple Glazing
Overview: Windows with two or three layers of glass, separated by an insulating gas.
Advantages:
- Insulation: Provides superior thermal insulation compared to single-pane windows.
- Noise Reduction: Helps reduce outside noise.
3.3 Gas Fills
Overview: The space between the panes of glass is filled with gases like argon or krypton.
Advantages:
- Energy Efficiency: Enhances insulation and reduces heat transfer.
3.4 Frame Insulation
Overview: Frames made from materials with insulating properties or with added insulation.
Advantages:
- Energy Efficiency: Improves overall window performance by reducing heat loss through the frame.
4. Installation Considerations
Proper installation is crucial for maximizing the performance and longevity of your new windows. Consider the following:
4.1 Professional Installation
- Benefits: Ensures correct installation, prevents issues like air leaks or water infiltration, and may be required for warranty coverage.
4.2 Custom vs. Standard Sizes
- Custom Windows: Necessary for non-standard window openings or specific design requirements.
- Standard Sizes: More cost-effective and quicker to install if your openings fit standard dimensions.
4. Permits and Regulations
- Local Codes: Check with local building codes and regulations to ensure compliance, especially for significant changes or large installations.
5. Budget and Financing
Window replacement costs can vary widely based on material, style, and installation complexity. Here are some budgeting and financing tips:
5.1 Budget Planning
- Cost Factors: Consider the cost of materials, labor, and any additional features such as energy-efficient glass.
- Quotes: Obtain quotes from multiple contractors to compare prices and services.
5.2 Financing Options
- Home Improvement Loans: Explore financing options such as personal loans or home equity lines of credit.
- Manufacturer Rebates: Check for any available rebates or incentives from window manufacturers.
6. Conclusion
Choosing the right window replacement options involves considering materials, styles, energy efficiency, and installation factors. By understanding the various types of windows and their benefits, you can make an informed decision that enhances the functionality, appearance, and energy performance of your home. Whether you prioritize aesthetics, energy savings, or durability, selecting the right windows and ensuring professional installation will contribute to the overall success of your window replacement project.
Explore
Everything You Need to Know About Window Replacement: Costs, Options, and Top Installers
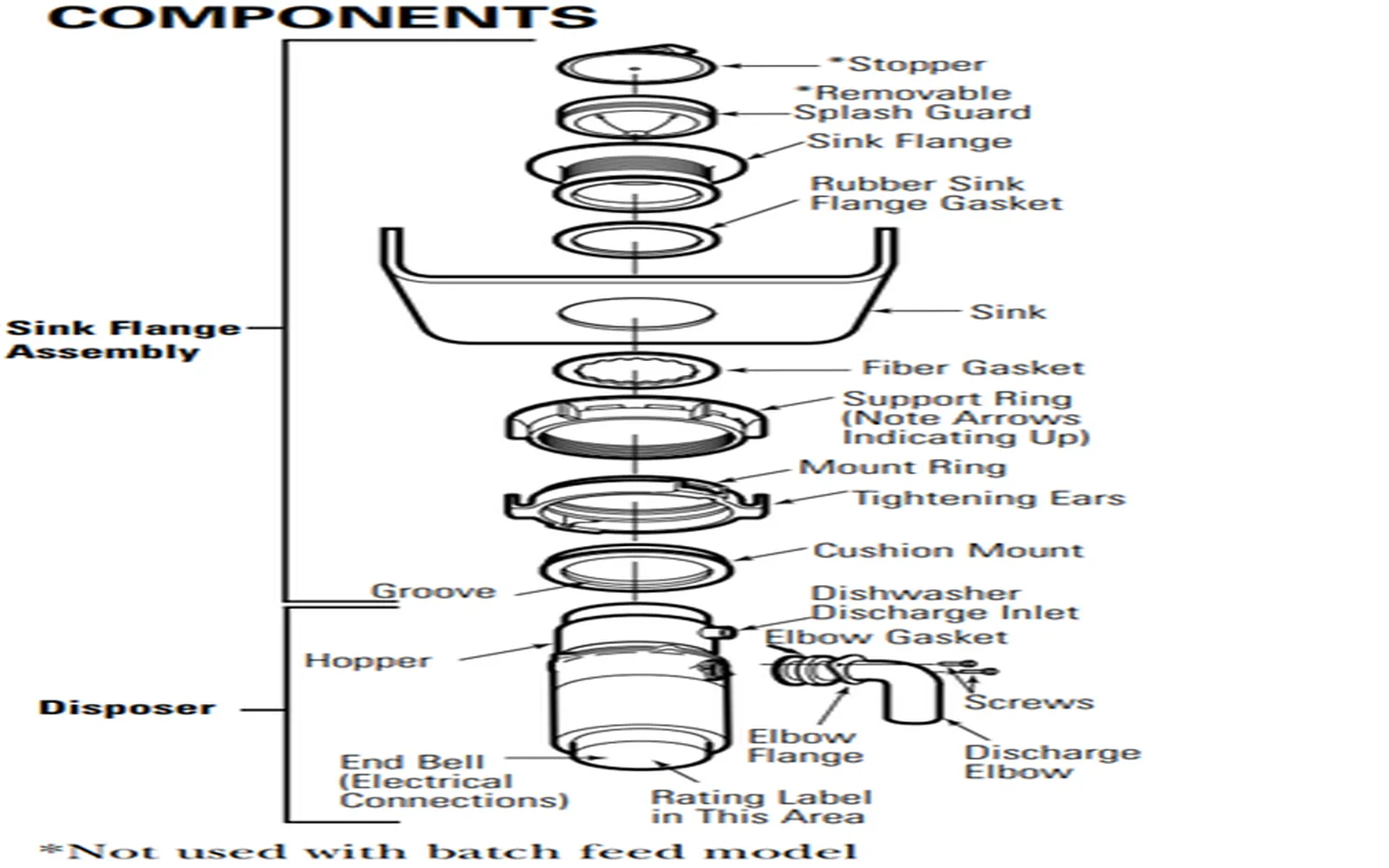
Garbage Disposal Replacement: How Much Does It Cost?

Finding the Right Window Installers for Your Home

Comprehensive Guide to Student Loan Assistance Options: Find the Right Help for Your Education Debt

Comprehensive Guide to Humana Health Coverage Plans: Benefits, Options, and Enrollment Tips

Discover the Best Cell Phone Plans: Your Guide to Affordable and Flexible Options
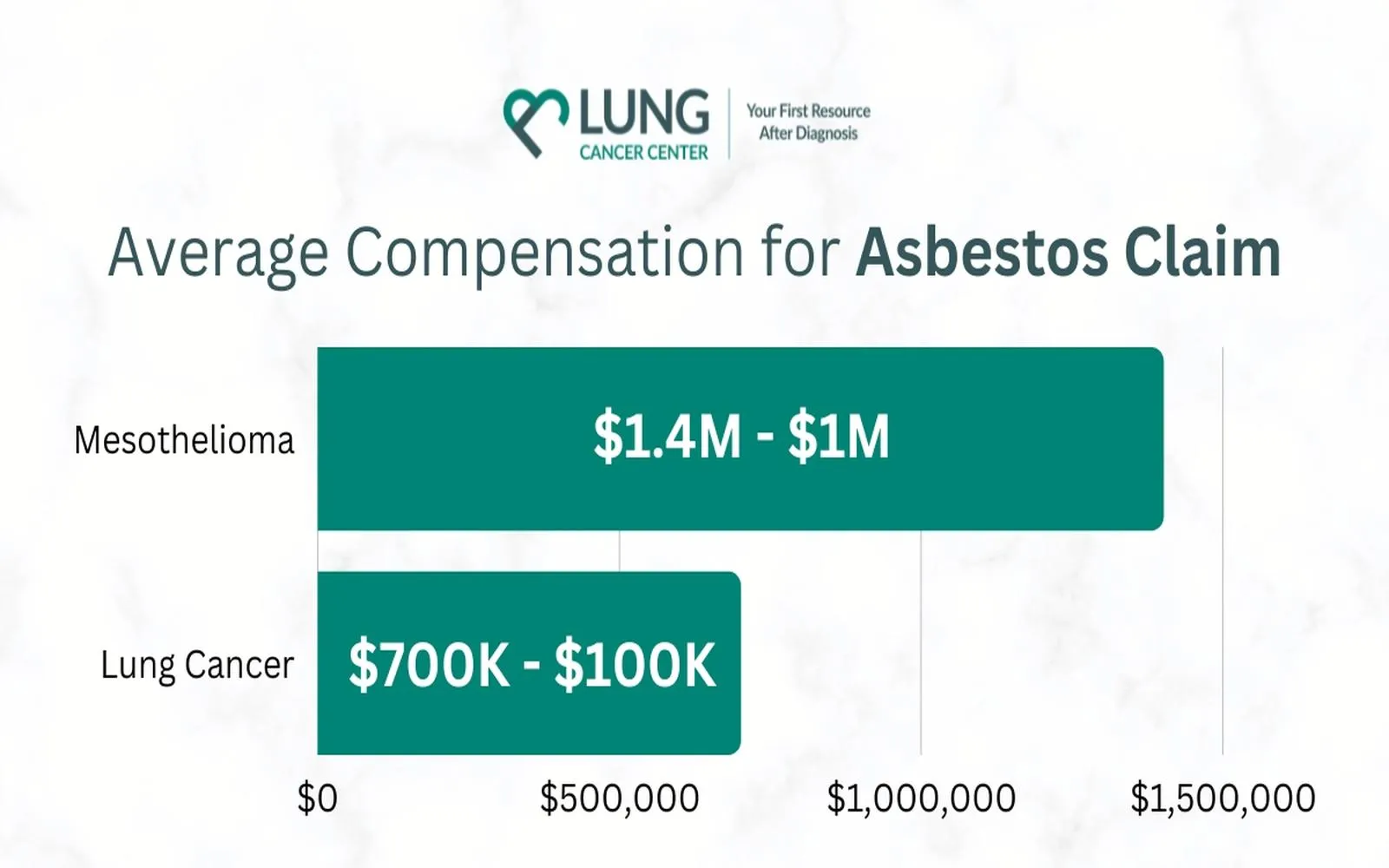
Maximizing Mesothelioma Compensation: Legal Options & Financial Recovery

Top 10 Best Cell Phone Plans of 2023: Affordable Options for Every Budget
