Data Protection: Safeguarding Information in a Digital World
In today’s increasingly digital landscape, data protection has become a critical priority for individuals, businesses, and organizations. With vast amounts of sensitive and personal information being collected, stored, and processed online, safeguarding this data is essential to ensure privacy, prevent breaches, and comply with legal and regulatory requirements.
What is Data Protection?
Data protection refers to the process of safeguarding data from unauthorized access, corruption, or loss, ensuring its integrity and confidentiality. This involves implementing a range of security measures, policies, and technologies to protect data both at rest (stored data) and in transit (data being transferred over networks). It is a vital part of any organization's information security strategy.
Why is Data Protection Important?
Data protection is essential for several reasons:
- Privacy: Protecting personal information to ensure individuals’ privacy is maintained.
- Security: Preventing unauthorized access or cyber-attacks on sensitive data.
- Compliance: Meeting legal and regulatory requirements to avoid fines and penalties.
- Trust: Building consumer confidence by demonstrating a commitment to data protection.
- Business Continuity: Ensuring that important data is secure and recoverable in the event of an incident.
Key Principles of Data Protection
- Confidentiality: Ensuring that sensitive data is only accessible to authorized users.
- Integrity: Ensuring data remains accurate and unaltered unless done so by authorized personnel.
- Availability: Ensuring that data is accessible and usable by authorized individuals when needed.
- Accountability: Organizations must be accountable for managing and protecting data throughout its lifecycle.
Types of Data Protection Measures
- EncryptionEncrypting sensitive data ensures that even if it is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the decryption key. This is crucial for both stored data and data in transit.
- Access ControlLimiting who can access certain data is critical. Access controls can be enforced using authentication methods like passwords, biometrics, or multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Data MaskingData masking involves replacing sensitive data with non-sensitive equivalents to protect it during testing or analysis while maintaining data integrity.
- Data BackupRegular backups help ensure that data can be restored in the event of data loss due to cyber-attacks, natural disasters, or system failures.
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)Firewalls and IDS monitor and block unauthorized access attempts to network systems, preventing data breaches from external sources.
- Data MinimizationLimiting the amount of data collected and retaining it only as long as necessary for business purposes can reduce the risk of exposure.
- Regular Audits and MonitoringConducting periodic audits and continuous monitoring ensures that data protection measures remain effective and up to date.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
Several laws and regulations globally address the need for data protection. These laws are designed to ensure that organizations manage and process personal data responsibly, protecting individuals' privacy rights.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)GDPR is one of the most stringent data protection laws in the world. It applies to organizations operating in the European Union (EU) or processing the personal data of EU citizens. It establishes strict rules on data collection, processing, consent, and rights for individuals, including the right to be forgotten.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)CCPA applies to businesses that collect personal data from California residents. It grants consumers rights related to their personal data, including the right to opt out of data sales, access their data, and request deletions.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)HIPAA regulates the privacy and security of health-related data in the U.S. for organizations that deal with medical records or personal health information (PHI).
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)PCI DSS outlines security standards for businesses that process credit card information, focusing on preventing credit card fraud and data breaches.
- Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA)FISMA mandates that federal agencies and contractors in the U.S. implement specific cybersecurity measures to protect government data.
Data Protection Strategies for Organizations
Organizations must develop comprehensive data protection strategies that include both preventive and corrective measures. Here are a few key strategies:
- Data ClassificationClassifying data based on its sensitivity helps determine which protection measures to apply. Sensitive data requires stricter controls than non-sensitive data.
- Employee Training and AwarenessEducating employees on data protection policies and best practices reduces human error, which is one of the most common causes of data breaches.
- Incident Response PlansOrganizations should have an incident response plan in place to quickly address and mitigate the effects of a data breach or other cybersecurity event.
- Third-Party Risk ManagementAssessing and monitoring third-party vendors and service providers ensures that they meet required data protection standards, especially when they have access to sensitive data.
- Data AnonymizationAnonymizing data ensures that personal identifiers are removed, making it difficult to link data to an individual in the event of a breach.
The Role of Data Protection in the Future
As technology continues to evolve, the volume and variety of data generated will increase. Protecting this data becomes even more critical as new threats and vulnerabilities emerge. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being incorporated into data protection systems to identify and respond to threats more proactively.
Furthermore, as more organizations shift to cloud-based solutions and remote working environments, data protection strategies must adapt to ensure that data remains secure both in transit and at rest.
Conclusion
Data protection is not only a legal requirement but a crucial part of maintaining trust with customers, clients, and employees. Organizations that prioritize data security are better equipped to prevent breaches, mitigate risks, and comply with regulations. With data becoming a core asset in the modern economy, protecting it effectively will continue to be a key concern for businesses across industries.
Explore

Ultimate Guide to Secure Data Protection Services: Safeguard Your Sensitive Information
Top Cloud Security Providers: Safeguarding Your Data in the Digital Age

Guarding Your Digital Fortress: Essential Data Protection Services for a Safer Tomorrow

Data Security Management: Essential Strategies for Protection

Affordable Cloud Security: Protect Your Data Without Breaking the Bank

Best Cloud Security Services to Protect Your Business Data

Top 10 Reliable Cloud Backup Services: Secure Your Data with Confidence
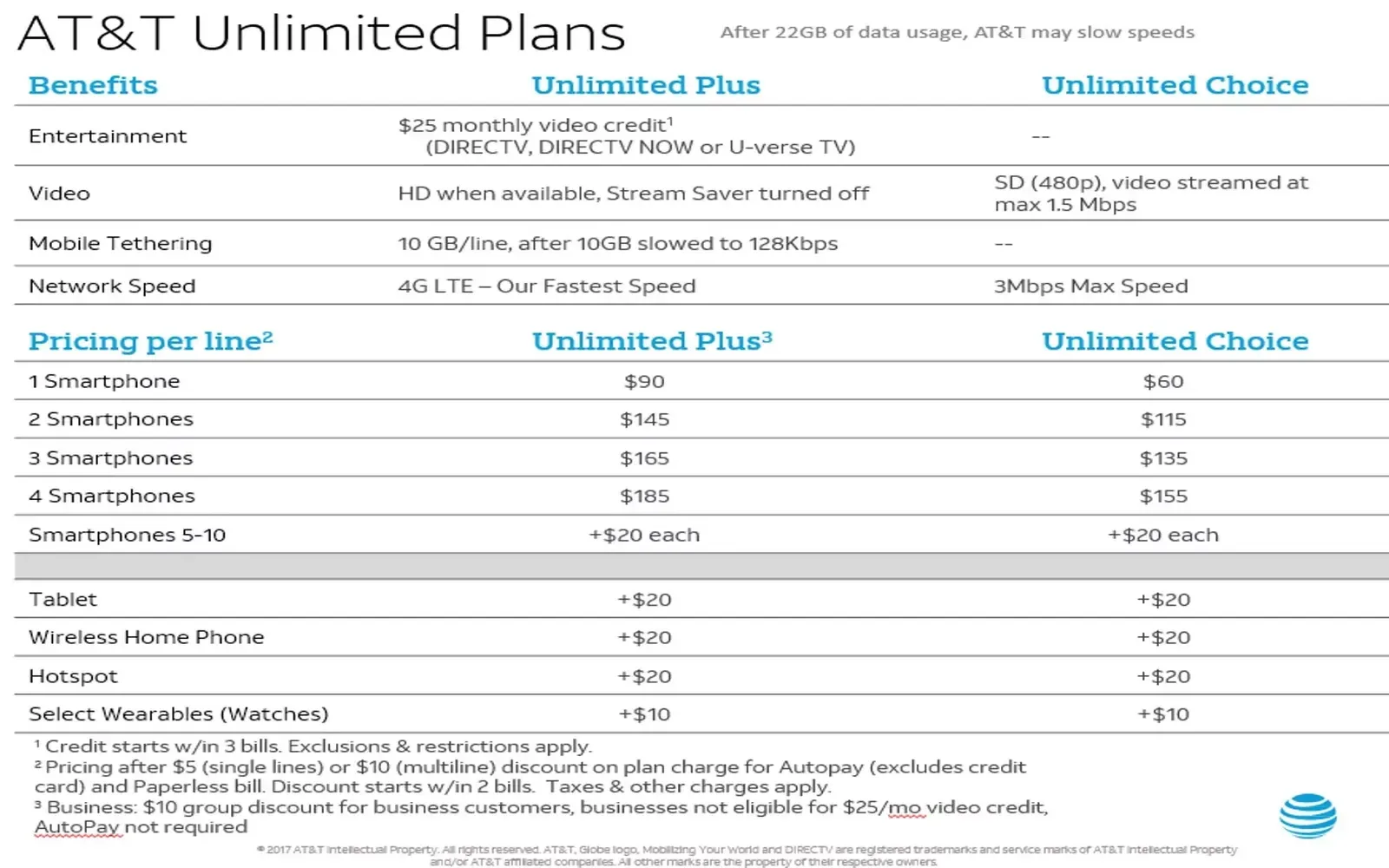
Top 10 Best Unlimited Data Plans: Uninterrupted Browsing and Streaming!
